Resident vs. Non-resident
Taxpayers who are liable to pay income tax on his/her income, are classified into Resident and Non-resident in terms of whether Korea has the taxation liability on his/her worldwide or just domestic income, and the scope of income deduction pursuant to the provisions of Income Tax Act of Korea.Residents(D7, D8 and D9 visa holding for expats) are required to file all income derived from inside and outside of Korea from their first working days regardless 183days. However, in case of foreign source income of a foreign resident whose sum of period of having a domicle or place of residence in Korea is five years or less for 10 years retroactively from the last day of the relevant period, only the income derived to work in Korea shall be taxed.
Non-resident is liable to pay income tax only on the income derived from sources within Korea in case he/she stays longer than 183days(total number of per calendar year).
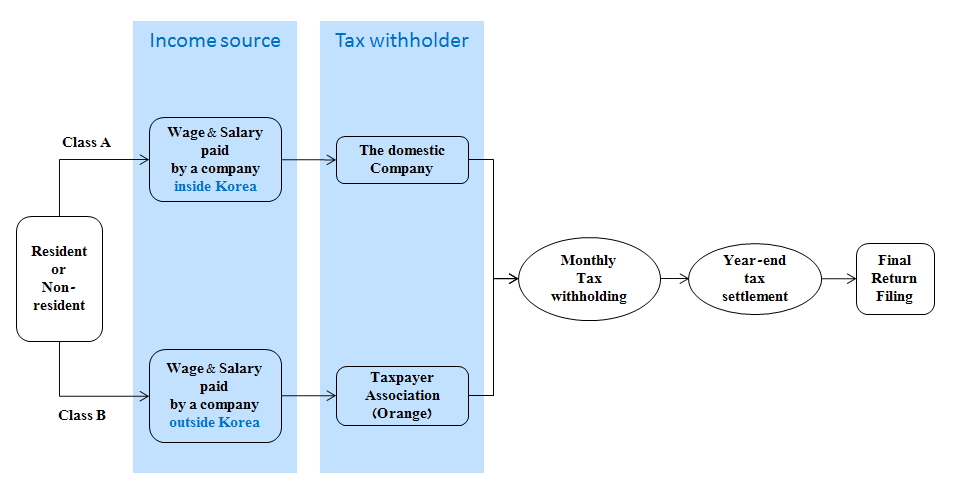
Income tax withholder
Income paid by a company inside Korea A resident or non-resident who has wage & salary income from a company inside Korea shall file his/her tax return and pay the relevant tax amount to the government through the company he/she works for.Income paid by a company outside Korea In case he/she has income from a company outside of Korea he/she shall join a taxpayer association for taxation. The taxpayer association would be the tax-withholder and pay collected taxes to the National Tax Office monthly. As for a foreigner or non-resident who works longer than 183 days(or 6 months) for a financial year in Korea has income tax liability in Korea by the clause 4th of Income Tax Act. Please visit 'How to join' to join Orange if you haven't joined an association.
Taxable income(wage & salary, RS, RSU, Stock option, etc.)
Wage & Salary Income means salary, remuneration, annual allowance, allowance, bonus and any other allowances of a similar nature received in return for services. Taxation methods for non-resident who have wage & salary Income only are same as the Korean residents.For Korean residents, who are entitled for stock options(like RS, RSU, Stock option, etc.) from a company outside Korea, could pay income tax through a taxpayer association with benefits for 10% deduction of the calculated income tax.
Progressive rate tax vs. Flat rate tax
A progressive rate tax is a tax in which the tax rate increases as the taxable amount increases. Progressive rate taxes are imposed in an attempt to reduce the tax incidence of people with a lower ability to pay, as such taxes shift the incidence increasingly to those with a higher ability-to-pay. All local Koreans should pay taxes with this progressive rate. The opposite of a progressive tax is a flat rate tax. Expatriates or foreigners can choose one between progressive and flat.
A flat rate tax is a system of taxation where one tax rate is applied to all personal income with no deductions. Where a foreign executive officer or employee (excluding daily employed workers; hereinafter referred to as "foreign worker") begins to first provide labor in the Republic of Korea, on or before December 31, 2023, the amount of income tax on earned income that the foreign worker receives in return for his/her labor in the Republic of Korea may be calculated by multiplying the relevant earned income by 19/100 (or 19 percent).
How to pay taxes
You are a member of a taxpayer association? If so, send salary information(or pay slip by email) to the association so that it could calculate income tax to send you a tax invoice. The association will pay all taxes collected from taxpayers to the National Tax Office on 10th of the following month. Then the association will issue a certificate or receipt for the payment.3 percent Tax Deduction(credit)
If a taxpayer pays income tax using Progressive tax, he/she gets benefits for 3 percent tax deduction of the computed income tax.(so called Taxpayer Association Deduction). Flat tax doesn't allow any deductions.Avoid double taxation
Korea has income tax treaties with a number of foreign countries desiring to conclude a Convention for the avoidance of double taxation and the prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income. Once a foreign worker paid income tax in Korea, he/she will get tax deductions for the same amount taxes paid in Korea, or get tax exemption(especially for Norway). Please visit the National Tax Office to check countries engaged in agreement with Korea.Tax Penalties
If a resident or non-resident fails to file a tax return, or doesn't pay in full, penalties shall be charged at the following rates; Penalty on failure to tax returnPenalty on Non-payment or underpayment of taxFailure to file : 20 percent penalty of the calculated income tax Under-reporting : 10 percent of the calculated income tax
A penalty in the amount of 0.025 to 0.03 percent of the amount shall be added to the amount of the tax due, for each day the amount remains unpaid.
Visa renewal for foreigners
Most of D7 to D9 visa holders are requred to renew their visa every year. Certificates issued by a taxpayer association is one of the required documents for the visa renewal.Global Income Tax Filing
If a taxpayer missed joining a taxpayer association and didn't clear tax liability within a fiscal year, he/she can pay income taxes by Global Income Tax Filing with no penalty in May of the following year. However, the Global Income Tax Filing doesn't allow 10 percent tax deduction or credit(so called Taxpayer Association credit).If you need further information for Korean income tax or how to pay, please do not hesitate to contact us.
